Cables are at the heart of modern technology, powering everything from household appliances to advanced electronics.
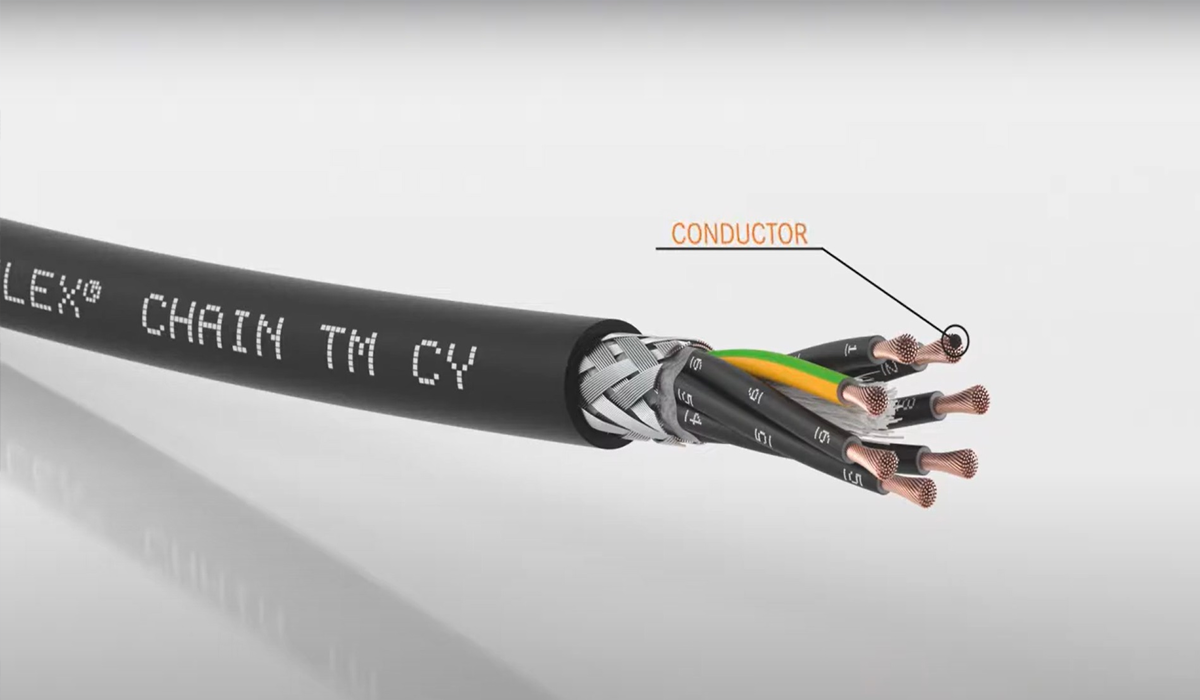
As devices become smaller and more sophisticated, traditional rigid cables no longer meet the demands of innovation. This is where ultra thin flexible cables come in a breakthrough design that can endure extreme bending while maintaining performance. These cables are transforming electronics, robotics, and wearable technology by enabling compact, durable, and highly adaptable connections. In this It’s Time to Think About Wire media will explore the next generation of cable innovations that are poised to redefine how we connect
Understanding Ultra-Thin Flexible Cables
Ultra-thin flexible cables are crafted with tiny diameters but remarkable mechanical strength. Typically, they consist of conductive metals like copper or silver combined with elastic polymers that act as insulation. This combination allows the cables to bend, roll, or twist repeatedly without breaking or losing performance.
Unlike conventional rigid cables, ultra-thin variants are designed to adapt to complex shapes in modern devices. This makes them ideal for slim smartphones, compact wearable devices, and even miniaturized robotics. The innovation behind these cables lies in their ability to maintain high conductivity and durability despite their small size.
Materials and Technology Behind Flexibility
The secret to ultra-thin cable resilience is advanced material engineering. Metals like copper or silver are paired with elastic polymers, allowing the cable to endure hundreds of thousands of bending cycles without damage. Some designs even incorporate nano-wire technology, improving electrical performance while enhancing durability.
Insulating layers are made from elastomeric materials that protect the core from physical stress, friction, and environmental factors. This makes the cables suitable for extreme conditions, including industrial robotics and medical devices, where reliability is crucial.
Read Also: Rethinking Cable Media: A Profitable Modern Business Model
Applications in Robotics and Wearables

In robotics, ultra-thin flexible cables allow smooth and precise movement of mechanical parts. They can transmit power and signals without restricting joint motion, which is essential for humanoid robots and robotic arms. The flexibility ensures that cables do not wear out quickly, even with continuous motion.
Wearable technology also benefits greatly. Smartwatches, health-monitoring sensors, and smart clothing rely on thin, flexible wiring to remain comfortable and unobtrusive. These cables bend with the body, preventing breakage while extending the life of the device.
Advantages Over Traditional Cables
One major advantage is extreme bend resistance. Conventional cables weaken and lose conductivity after repeated bending, while ultra-thin cables stay reliable. Their lightweight and compact form factor also simplifies installation in tight spaces and allows more efficient electronic layouts.
Flexible cables reduce maintenance costs by minimizing cable failure and device downtime. This is especially important for high-tech equipment that requires constant operation, such as medical devices or industrial machinery. Moreover, ultra-thin cables support modern electronics’ trend toward smaller, lighter, and more durable products. Their performance and adaptability provide designers with greater freedom to innovate without worrying about physical constraints.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite their advantages, ultra-thin flexible cables face challenges. Manufacturing costs are higher than traditional cables due to advanced materials and precision processes. Extremely thin designs may also struggle with heat dissipation and high-current capacity.
However, research continues to improve materials and production methods. Future developments may include even thinner, stronger, and more energy-efficient cables suitable for wearable medical devices, robotics, and electric vehicles.
Thanks for reading! Stay tuned for more groundbreaking insights at It’s Time to Think About Wire media.
Image Source:
First Image from wesbellwireandcable.com
Second Image from wire-media.com